Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation genetic testing is an integral part of assisted reproductive technologies (ART) contributing to an early form of prenatal diagnosis to identify abnormal and normal embryos (before transfer)
PGT-A
(Preimplantation Genetic Testing- Aneuploidy)
It screens for all the 23 pairs of chromosomes in the embryo and checks for additional, abnormal or missing chromosomes (Aneuploidy). PGT-A enables to choose and transplant embryos with standard chromosome number (Euploid embryos), thus reducing risk for chromosomal disorders in a pregnancy.

Conditions that PGT-A can detect
PGT-A
-
All chromosomal aneuploidies, the most common are:
Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)
Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13)
Edward syndrome (Trisomy 18) -
Sex chromosomal aneuploidies such as:
Turner syndrome (Monosomy X or X0)
Klinfelter syndrome (XXY)
XXX (Trisomy X) - Segmental Gain and Losses (>20Mb) in chromosomes which can lead to abnormalities in the embryo
Why is it important to have the PGT-A test?
- Increases success rate for transferring a single embryo.
- Decreases the risk of miscarriage caused by Aneuploidies.
- Boosts the chances of reproductive success in women over the age of 35.
At which stage can the PGT-A test be conducted?
- The PGT-A test is done when the embryo is 3 to 5 days old, post-fertilization. This stage provides enough cells for DNA extraction, allowing for successful testing and detection of mosaicism in Aneuploidies. Post-biopsy vitrification of embryos aids in planning optimal implantation conditions.
PGT-A is offered to:
- Couple with recurrent pregnancy losses
- Anyone opting for IVF pregnancy
- Couples who are facing IVF failures inspite of favorable conditions
- In case of IVF in advanced maternal age (>35 years)
- Known history of chromosomal aneuploidy
How is Setgene PGT-A better?
- PGT-A based on sequencing offers greater resolution, enabling the detection of segmental deletions and duplications.
- Advanced sequencing technology known for delivering sensitive and consistent outcomes.
- Flexible to meet individual needs, maintaining high quality.
- We provide end-to-end support: From result data interpretation, phenotype correlation to genetic counselling.
Setgene’s technology for PGT-A & What’re the benefits?
SETGENE PGT-A employs cutting-edge Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) technology.
- Quick and user-friendly.
- Analyses all 23 chromosome pairs for abnormalities in a single test.
- Capable of identifying chromosomal gains and losses larger than 20 Mb.
- Offers high-resolution analysis, examining 1Mb segments for precise data.
- Exceptionally sensitive in identifying Aneuploidy (100% sensitivity).
- High levels of specificity and accuracy (99.98% specificity).
- Reduced risk of test failure using NGS technology.
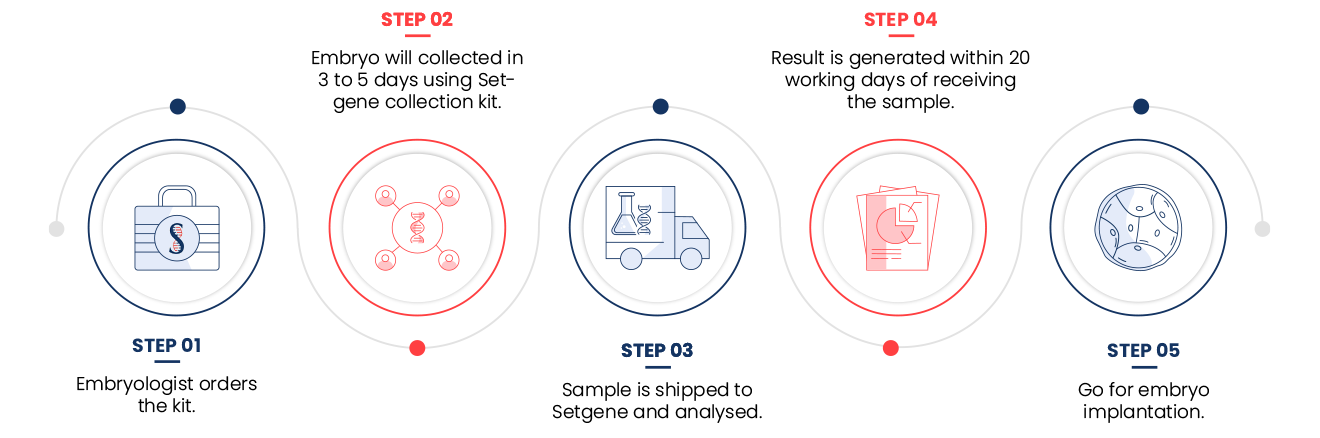
Setgene PGT-A workflow
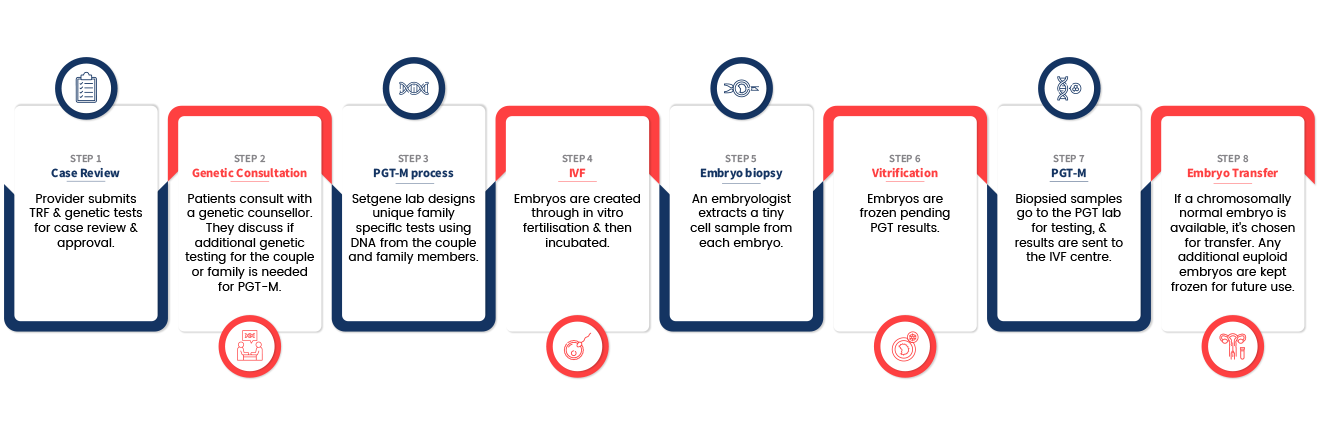
PGT - M
(Preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic disorders)
PGT-M is offered to:
Preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic disorders means testing the embryos for single gene disorders or inherited disorders. PGT-M is recommended to couples who are carriers and are at increased risk of inheriting a specific genetic disorder to their offspring.
- Both the partners are carriers of the same autosomal recessive condition, such as Thalassemia, Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle cell anemia, Tay-Sachs disease and many more.
- In case of carrier of a X-linked disorder like Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Hemophilia, Fragile-X syndrome
- Either of the partner has an autosomal dominant condition, for example, Huntington's disease, Achondroplasia
- History of previous child affected with a single gene disorder
- Interest in HLA matching for potential treatments.
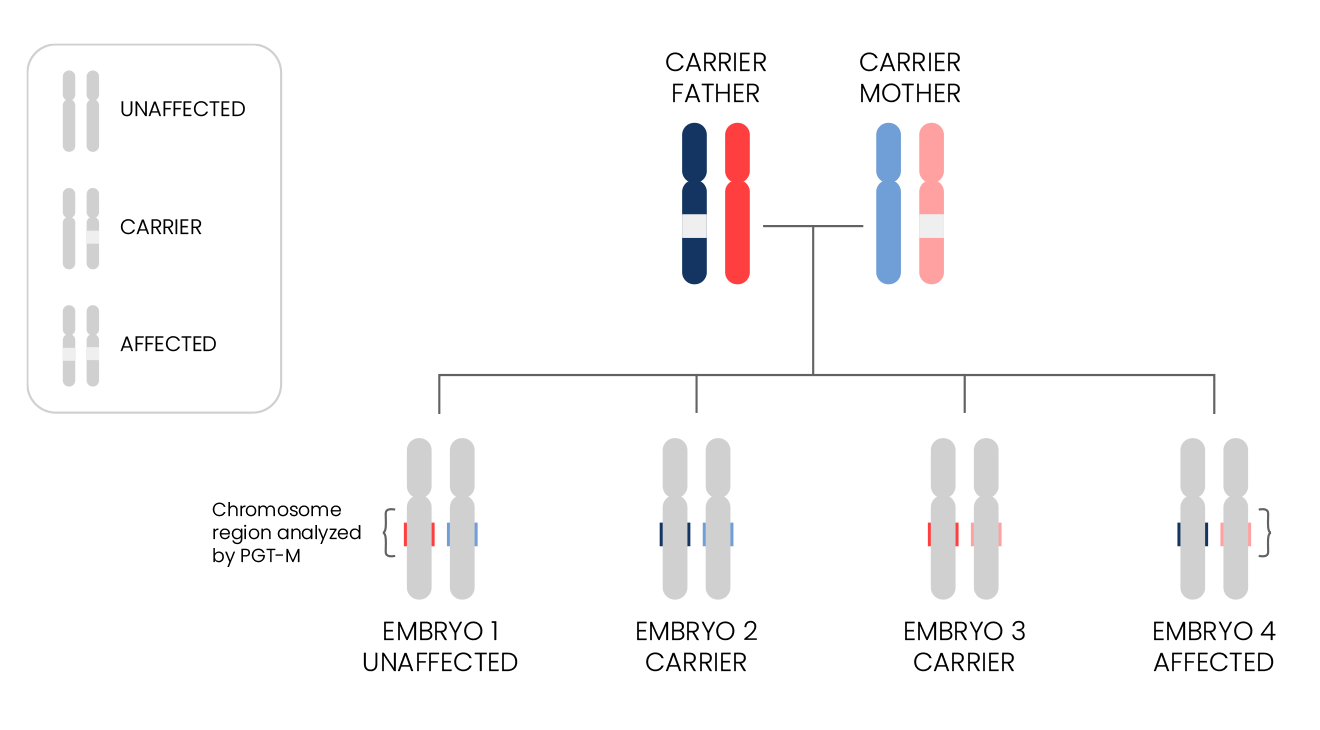
- PGT-M testing entails a detailed analysis of the specific mutation a person carries and the surrounding chromosomal region, as indicated by the coloured segment on each chromosome.
- The design of each PGT-M test is uniquely tailored to the specific family, requiring DNA samples from both partners and frequently from other family members to create a personalised test.
- Linkage analysis is then employed to identify the "genetic fingerprint" of the mutation, which helps in determining whether each tested embryo is affected or unaffected by the condition.
Setgene PGT-M workflow
PGT-SR
(Preimplantation genetic testing for structural rearrangements)
PGT-SR is offered to:
Detects chromosomal rearrangements, such as unbalanced translocations, which put embryos at risk of abnormal chromosome numbers or structures.
When either of the partners is carrier of a chromosomal structural rearrangement, such as:
- When either of the partners is carrier of a chromosomal structural rearrangement, such as:
- A reciprocal translocation, involving the exchange of segments between two non-homologous chromosomes.
- A Robertsonian translocation, where two particular chromosomes join together.
1. Reciprocal Translocations:
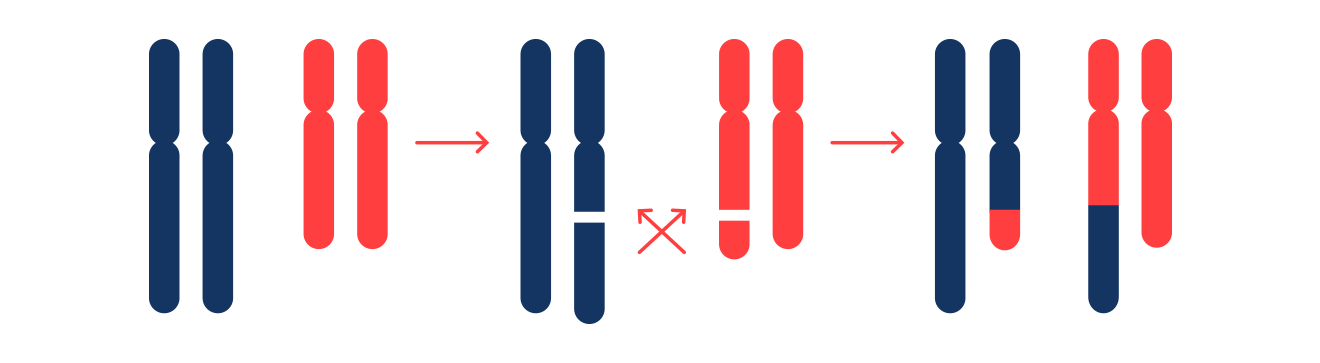
- Reciprocal translocations happen when segments of genetic material detach from two distinct chromosomes and exchange positions.
- Individuals who carry a balanced translocation may produce embryos with various chromosomal configurations: the same balanced translocation, an unbalanced version of the translocation (characterised by either a gain or loss of chromosomal material), or a completely normal chromosomal set.
- When one parent is a carrier of a reciprocal translocation, there's approximately an 80% likelihood that the resulting embryos will possess an incorrect amount of genetic material.
2. Robertsonian Translocations:
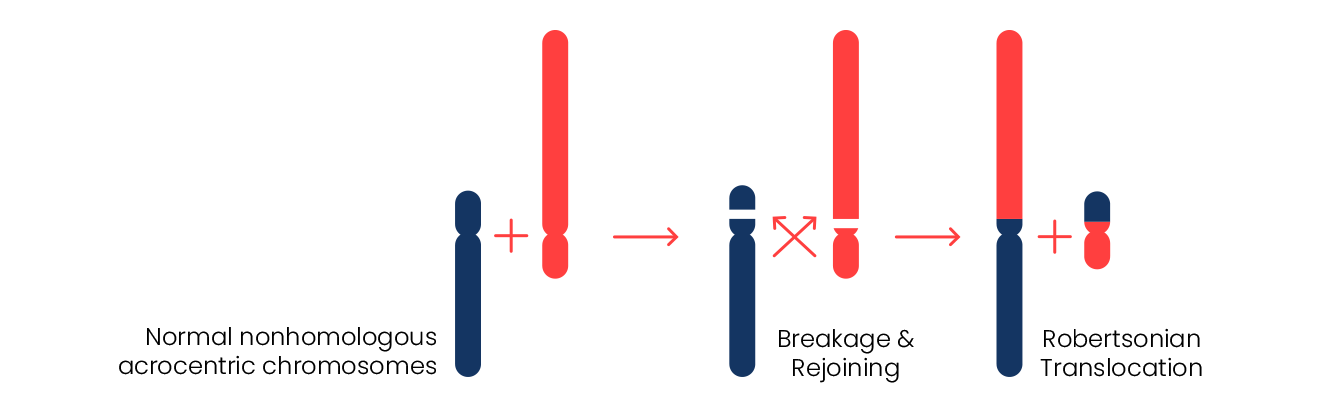
- Robertsonian translocations take place when two chromosomes fuse to create a single larger chromosome, resulting in a total chromosome count of 45 instead of the usual 46. This type of translocation most frequently involves chromosomes 13 and 14 or chromosomes 14 and 21.
- Such translocations can lead to conditions like Translocation Down Syndrome, trisomy 13, or uniparental disomy (UPD), where both copies of a chromosome come from the same parent.
3. Inversions:
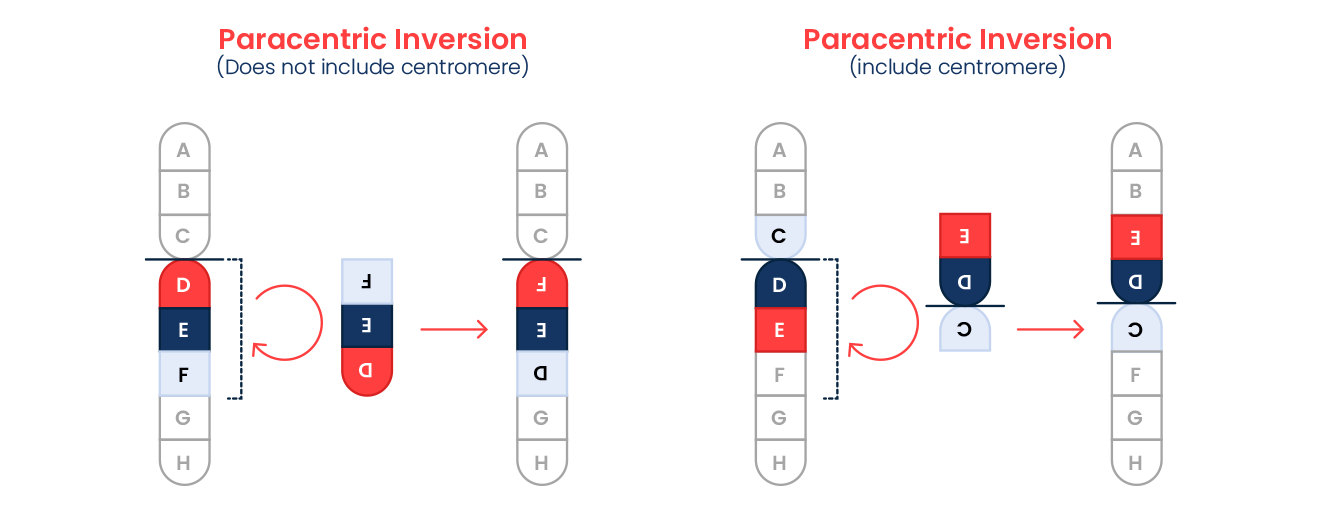
- Inversions are a type of chromosome rearrangement that affect a single chromosome. In such a case, a segment of the chromosome is reversed and reinserted in an inverted orientation.
- Individuals carrying an inversion may produce embryos with segments of chromosomes that are either missing or duplicated.
Setgene PGT-SR workflow
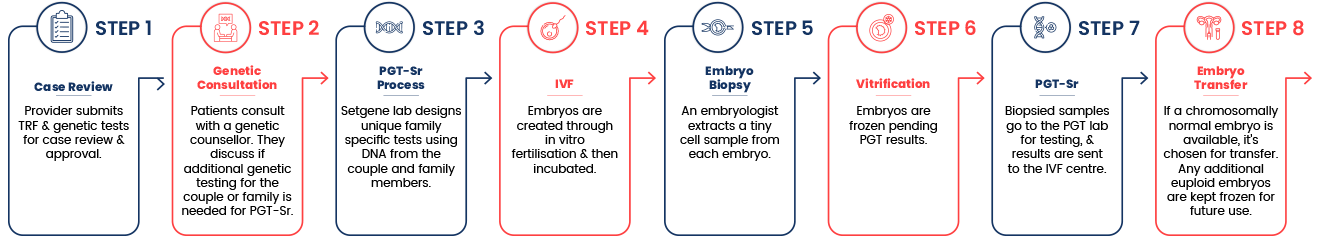
Why Setgene?
- PGT through sequencing offers greater resolution, enabling the detection of segmental deletions and duplications.
- Advanced sequencing technology known for delivering sensitive, specific and consistent outcomes.
- Flexible to meet individual needs, maintaining high quality.
- End-to-end support: Pre-test genetic Counselling 🡪 Testing 🡪Result data interpretation 🡪 Genotype-phenotype correlation 🡪Post-test genetic Counselling

