Clinical Exome
This testing is a targeted analysis designed for clinical applications, allowing for the identification of genetic variants associated with various medical conditions.

Which test to choose? & Criterias to choose the right test:
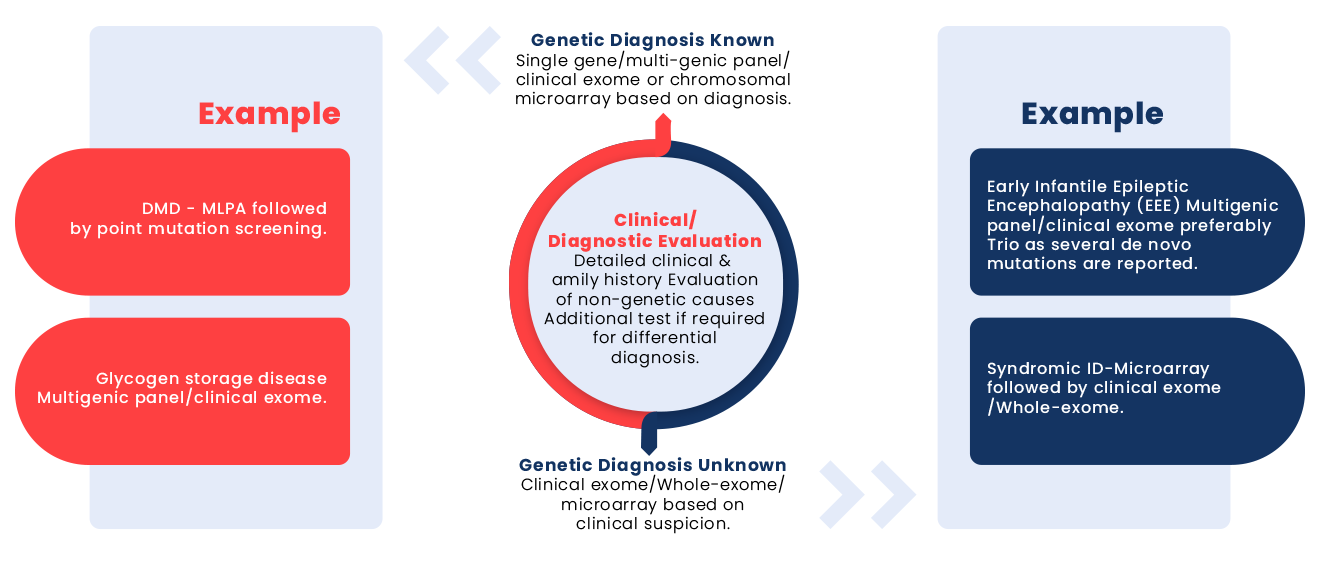
When To Offer Clinical Exome Sequencing:
- Suspected genetic causes based on clinical signs or family history.
- Screening for diseases with diverse genetic origins.
- Diagnosing unresolved genetic conditions.
- Guiding treatment and medical interventions.
- Reproductive planning and assessing recurrence risks.
- Prognostic evaluations related to family history.
Applicable for a range of disorders
- Rare Diseases
- Inherited Cancers
- Neurology
- Cardiology
- Endocrinology
- Nephrology
- ENT
- Others
Limitations
- All Clinical Exome orders encompass deletion/duplication (Del/Dup) analysis of genes with significant phenotypic impact. The assay typically does not detect single exon deletions or duplications, although they may be identified in certain cases. Del/Dup findings are reported at the exon level without analysis of breakpoint locations.
- While next-generation sequencing technologies and our bioinformatics methods greatly minimise the impact of pseudogenes or other similar sequences, these elements may still occasionally affect the assay's ability to accurately identify pathogenic variant alleles in both sequencing and deletion/duplication analysis.
- It's important to note the inherent limitations of the assay technology: it does not assess translocations, repeat expansions, large chromosomal rearrangements, or methylation.
Result Reporting
- Take a well-informed decision
- Comprehend any associated risks
- Engage in a discussion about the consequences of the results
- Connect them to relevant resources or support groups

